Understanding Zero Trust Security Architecture
Learn how Zero Trust principles can transform your organization's security posture and protect against advanced threats.
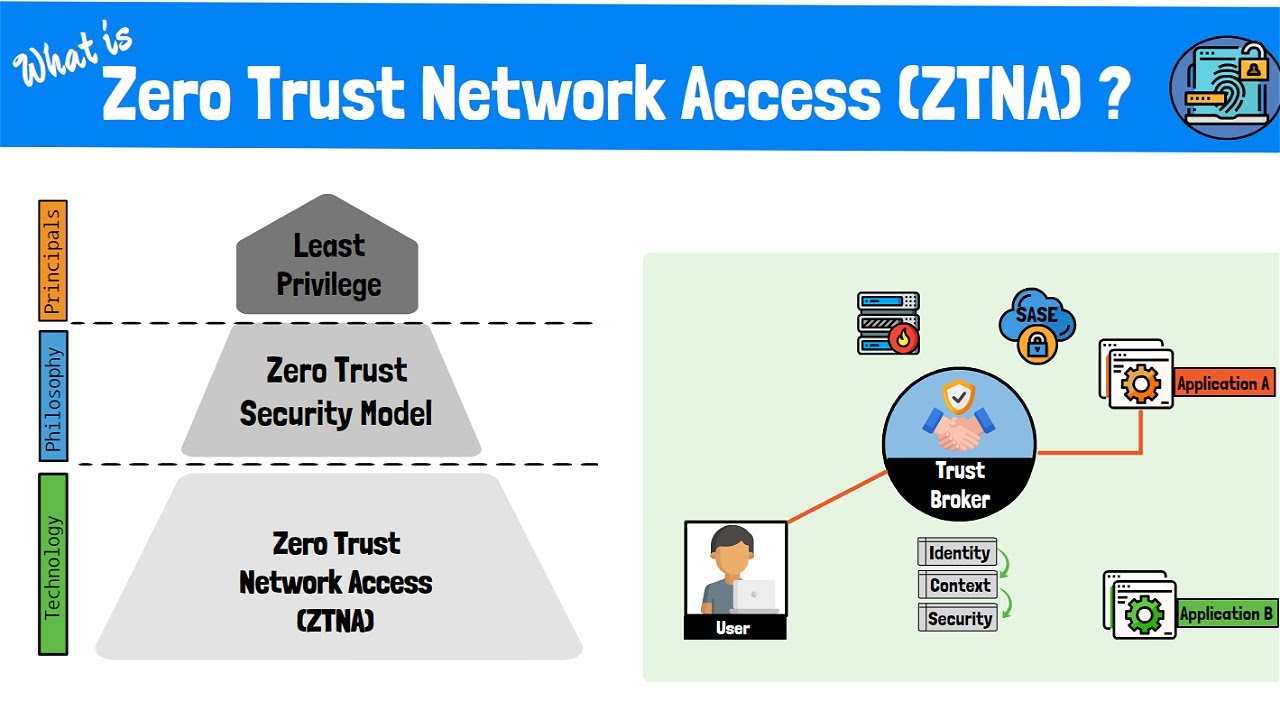
Zero Trust security has evolved from a buzzword to a fundamental security architecture that organizations worldwide are adopting to protect against sophisticated cyber threats. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, Zero Trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," fundamentally changing how we approach cybersecurity.
The Evolution Beyond Perimeter Security
Traditional security models relied on the concept of a secure perimeter, where anything inside the network was considered trusted and anything outside was considered untrusted. This castle-and-moat approach worked when most users and data resided within physical office boundaries. However, the modern digital landscape has rendered this model obsolete.
Why Traditional Security Models Fail:
Core Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
1. Verify Explicitly
Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, including user identity, location, device health, service or workload, data classification, and anomalies.
2. Use Least Privilege Access
Limit user access with just-in-time and just-enough-access (JIT/JEA), risk-based adaptive policies, and data protection to help secure both data and productivity.
3. Assume Breach
Minimize blast radius and segment access. Verify end-to-end encryption and use analytics to get visibility, drive threat detection, and improve defenses.
Building Blocks of Zero Trust Implementation
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
User Identity Verification:
Device Identity and Health:
Network Security and Micro-Segmentation
Software-Defined Perimeters:
Micro-Segmentation Strategies:
Data Protection and Classification
Data-Centric Security:
Zero Trust Data Access:
Application Security Integration
Secure Application Access:
API Security:
Zero Trust Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Months 1-3)
Phase 2: Identity and Access Foundation (Months 4-9)
Phase 3: Network Segmentation (Months 10-15)
Phase 4: Data Protection (Months 16-21)
Phase 5: Application Integration (Months 22-24)
Overcoming Zero Trust Implementation Challenges
Cultural and Organizational Challenges:
Solutions:
Technical Implementation Challenges:
Solutions:
Measuring Zero Trust Success
Key Performance Indicators:
Continuous Improvement:
The Future of Zero Trust
Zero Trust is not a destination but a journey of continuous improvement. As organizations mature their Zero Trust implementations, they're incorporating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automated response capabilities to enhance their security posture further.
Emerging Trends:
Zero Trust architecture represents a fundamental shift in how we think about cybersecurity. By implementing these principles and practices, organizations can build more resilient, adaptive security postures that protect against both current and future threats while enabling business agility and growth.
Related Articles

Essential Cybersecurity Practices for Small Businesses
Discover the fundamental cybersecurity measures every small business needs to implement to protect against modern threats and data breaches.

How to Protect Your Business from Phishing Attacks
Learn to identify and defend against phishing attempts that target your employees and sensitive business data.

The Complete Guide to Password Security
Master password best practices, two-factor authentication, and password management for enhanced security.
Need Expert Cybersecurity Guidance?
Our security professionals are here to help protect your business. Get a free consultation and vulnerability assessment.
